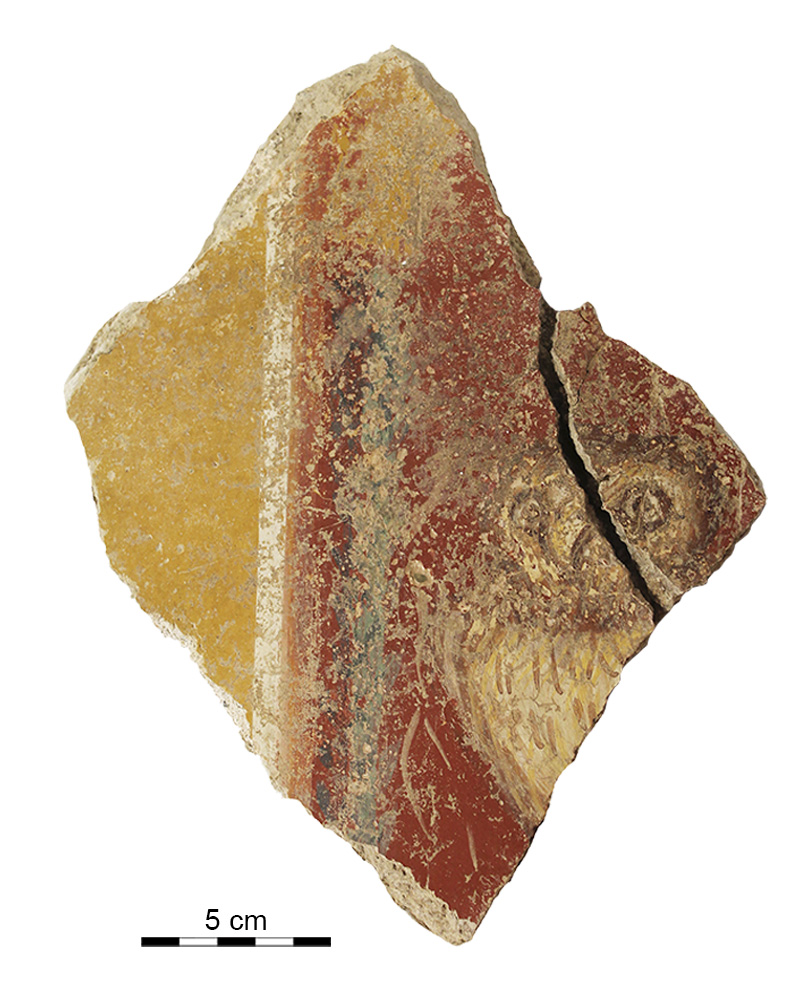
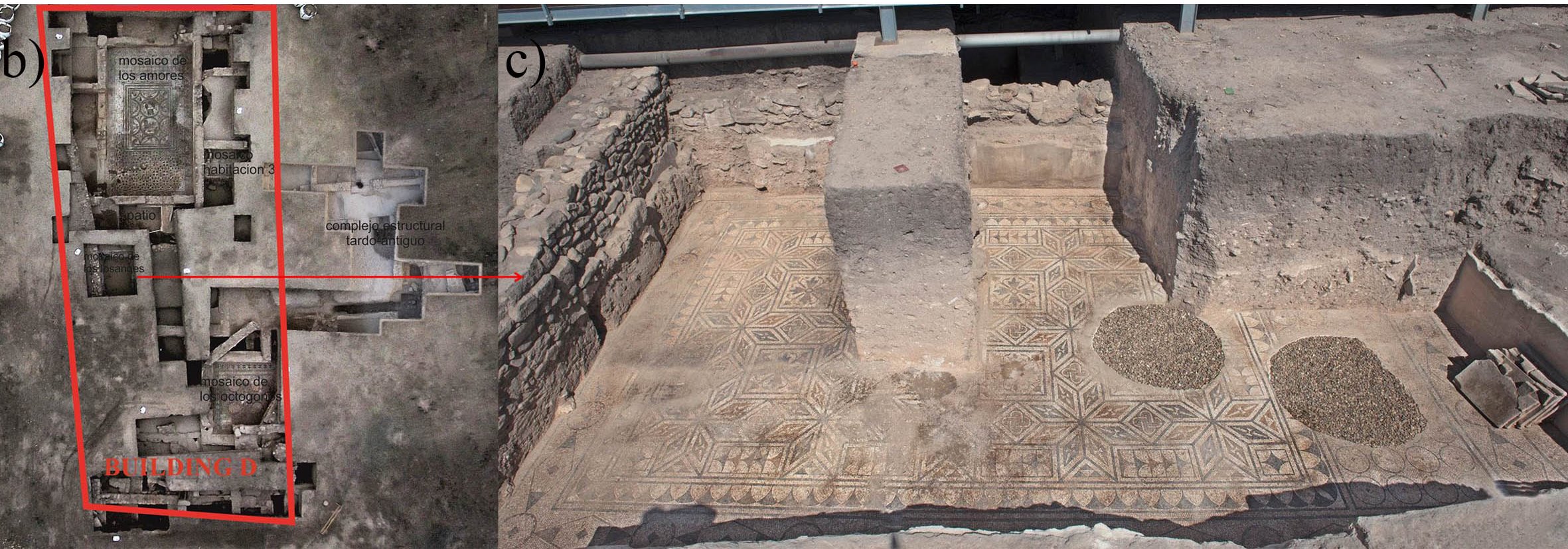
Wall fragment decorated with a owl (Cástulo, Linares, Spain)
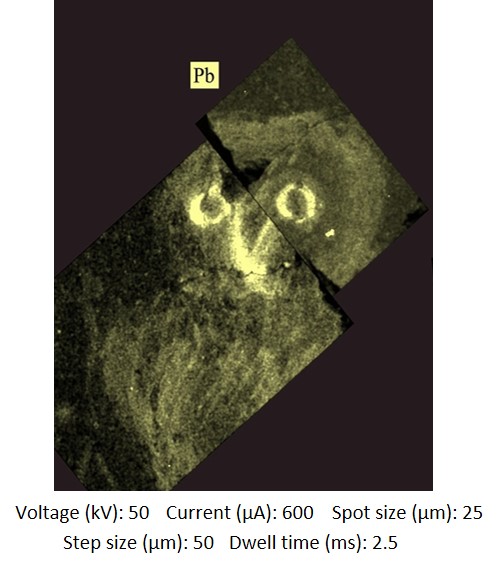
The results obtained from µEDXRF analysis, including the maps of surface composition (mapping), identified specific areas where a second type of yellow pigment with a significant amount of Pb (ca. 1 wt%) was used specifically in the beak and the eyes of the Little owl. This colour effect is hardly noticeable both for the surface decay (Raman spectra of Pb-based compounds could not be obtained) and for the small size of the figures. Still, the distribution maps of Pb clearly showed that, at least as regards the Little owl, the intention was to reproduce the typical shade of yellow of the beak and the sclerotic of the eye.
According to classical sources like Theophrastus, Vitruvius and Pliny the Elder, the yellow pigment may have been obtained heating lead white or cerussa ((PbCO3)2·Pb(OH)2) after submersion of lead in vinegar. The resulting lead white then transformed into various types of lead oxides in shades of yellow, fawn and red according to the time and temperature at which it was heated.
Dimensions
: 17 Centimeters
: 23.5 Centimeters
Materials
Painting
Temporal
: Roman
: Late 1st ct-2nd ct. AD
Spatial
: Cástulo
: Linares, Jaén, Spain
: WGS84
Copyrights
Creative Commons - Attribution, Non-Commercial, No Derivatives (BY-NC-ND)
References
Digital Resources
-
 Conjunto arqueológico de Cástulo-Forum MMX
Conjunto arqueológico de Cástulo-Forum MMX Creative Commons - Attribution, Non-Commercial, No Derivatives (BY-NC-ND)
Arquiberlab
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/ -
 Conjunto arqueológico de Cástulo-Forum MMX
Conjunto arqueológico de Cástulo-Forum MMX Creative Commons - Attribution, Non-Commercial, No Derivatives (BY-NC-ND)
Arquiberlab
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/ -
 Conjunto arqueológico de Cástulo-Forum MMX
Conjunto arqueológico de Cástulo-Forum MMX Creative Commons - Attribution, Non-Commercial, No Derivatives (BY-NC-ND)
Arquiberlab
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/ -
 Instituto Univesitario de investigación en Arqueología Ibérica. Universidad de Jaén
Instituto Univesitario de investigación en Arqueología Ibérica. Universidad de Jaén Creative Commons - Attribution, Non-Commercial, No Derivatives (BY-NC-ND)
Arquiberlab
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/ -
 Instituto Univesitario de investigación en Arqueología Ibérica. Universidad de Jaén
Instituto Univesitario de investigación en Arqueología Ibérica. Universidad de Jaén Creative Commons - Attribution, Non-Commercial, No Derivatives (BY-NC-ND)
Arquiberlab
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/ -
 Instituto Univesitario de investigación en Arqueología Ibérica. Universidad de Jaén
Instituto Univesitario de investigación en Arqueología Ibérica. Universidad de Jaén Creative Commons - Attribution, Non-Commercial, No Derivatives (BY-NC-ND)
Arquiberlab
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/ -
 Instituto Univesitario de investigación en Arqueología Ibérica. Universidad de Jaén
Instituto Univesitario de investigación en Arqueología Ibérica. Universidad de Jaén Creative Commons - Attribution, Non-Commercial, No Derivatives (BY-NC-ND)
Arquiberlab
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/ -
 Instituto Univesitario de investigación en Arqueología Ibérica. Universidad de Jaén
Instituto Univesitario de investigación en Arqueología Ibérica. Universidad de Jaén Creative Commons - Attribution, Non-Commercial, No Derivatives (BY-NC-ND)
Arquiberlab
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/ -
 Instituto Univesitario de investigación en Arqueología Ibérica. Universidad de Jaén
Instituto Univesitario de investigación en Arqueología Ibérica. Universidad de Jaén Creative Commons - Attribution, Non-Commercial, No Derivatives (BY-NC-ND)
Arquiberlab
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/ - Instituto Univesitario de investigación en Arqueología Ibérica. Universidad de Jaén
Creative Commons - Attribution, Non-Commercial, No Derivatives (BY-NC-ND)
Arquiberlab
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/ -
 Instituto Univesitario de investigación en Arqueología Ibérica. Universidad de Jaén
Instituto Univesitario de investigación en Arqueología Ibérica. Universidad de Jaén Creative Commons - Attribution, Non-Commercial, No Derivatives (BY-NC-ND)
Arquiberlab
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/
Activities
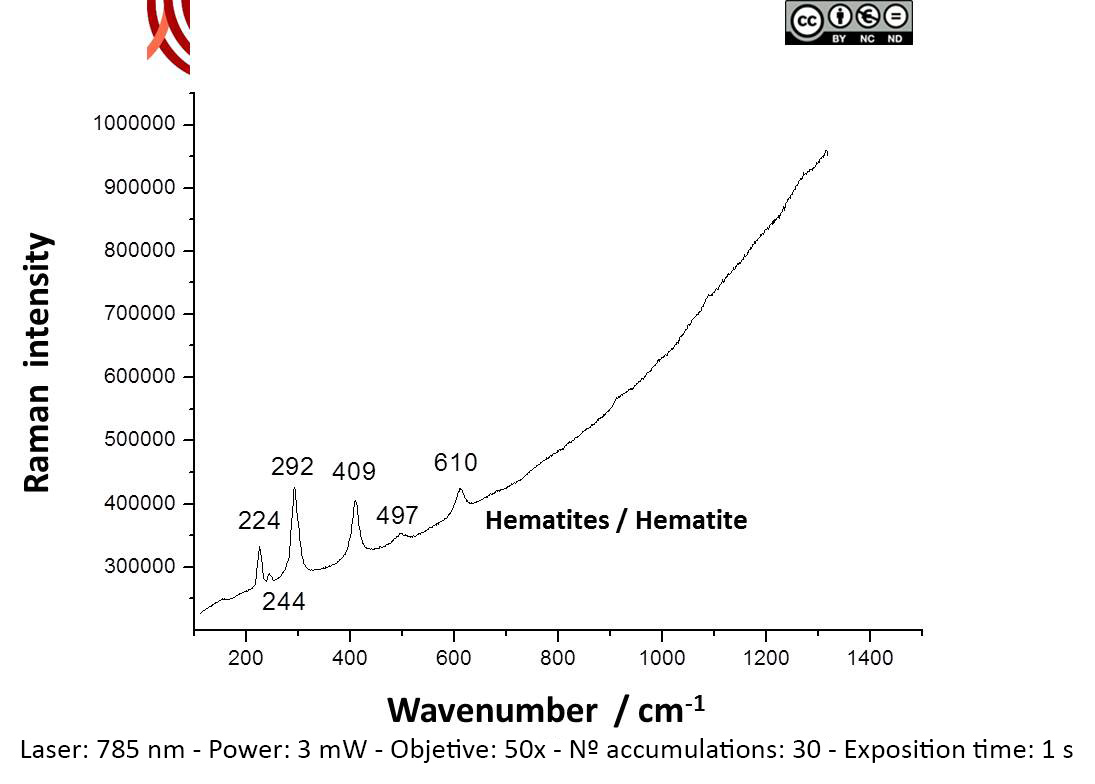
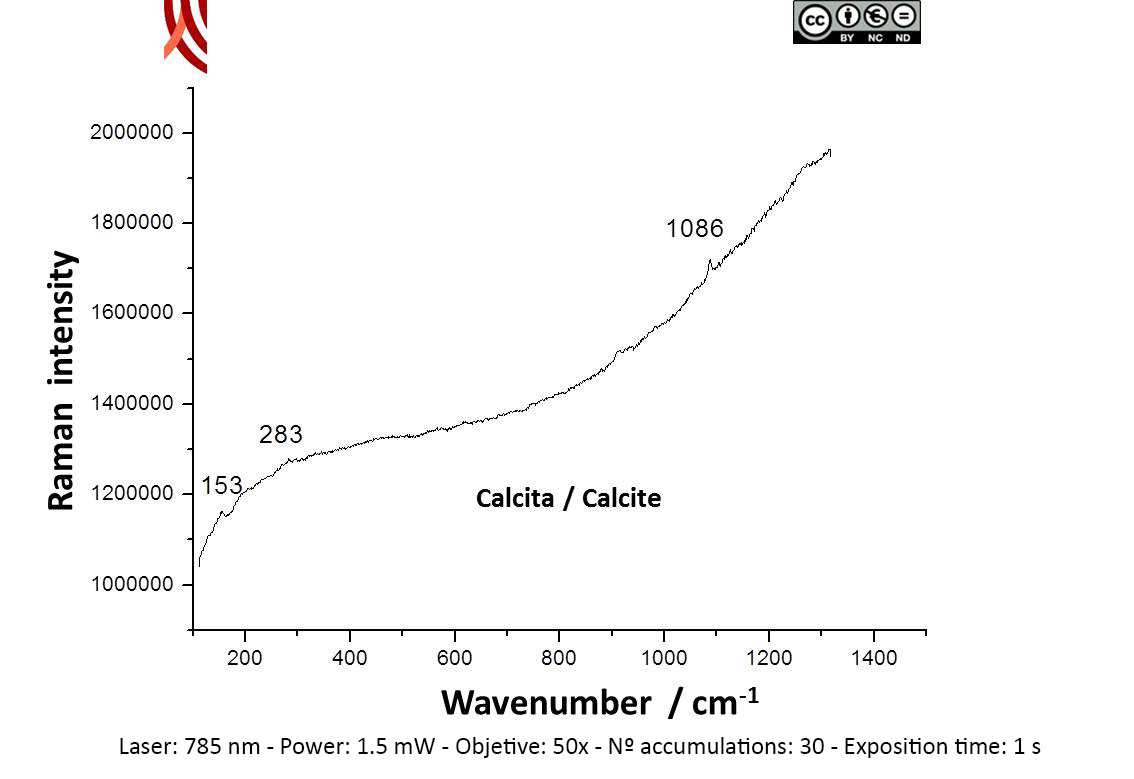
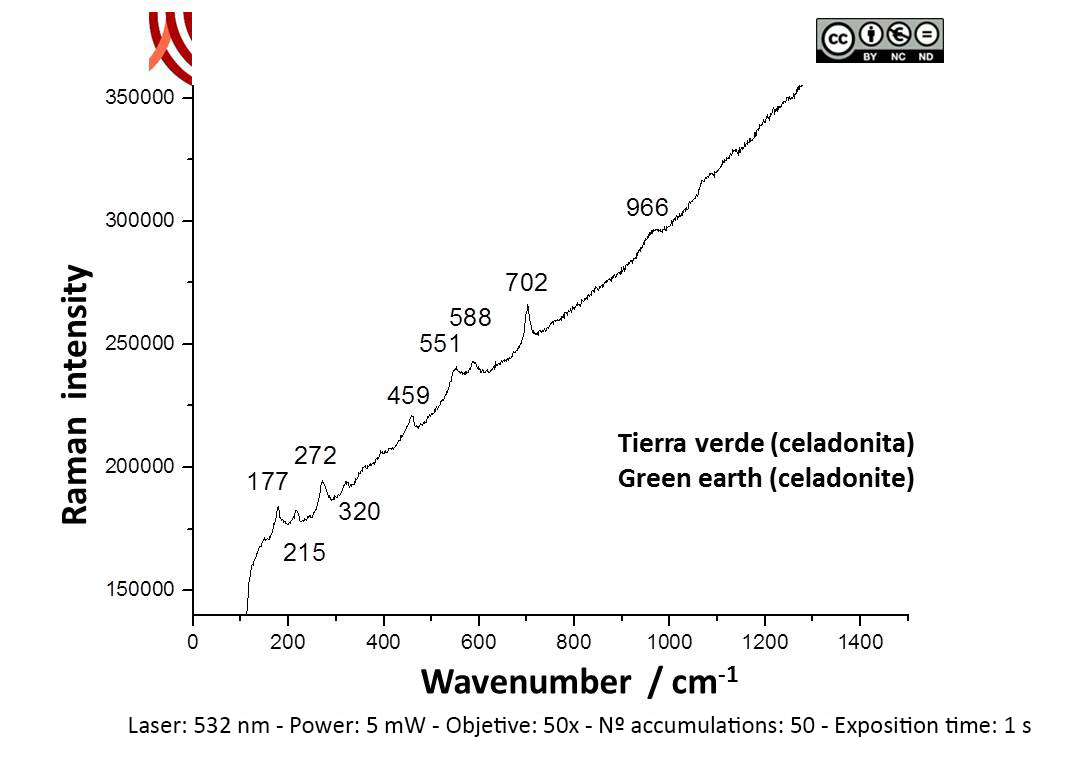
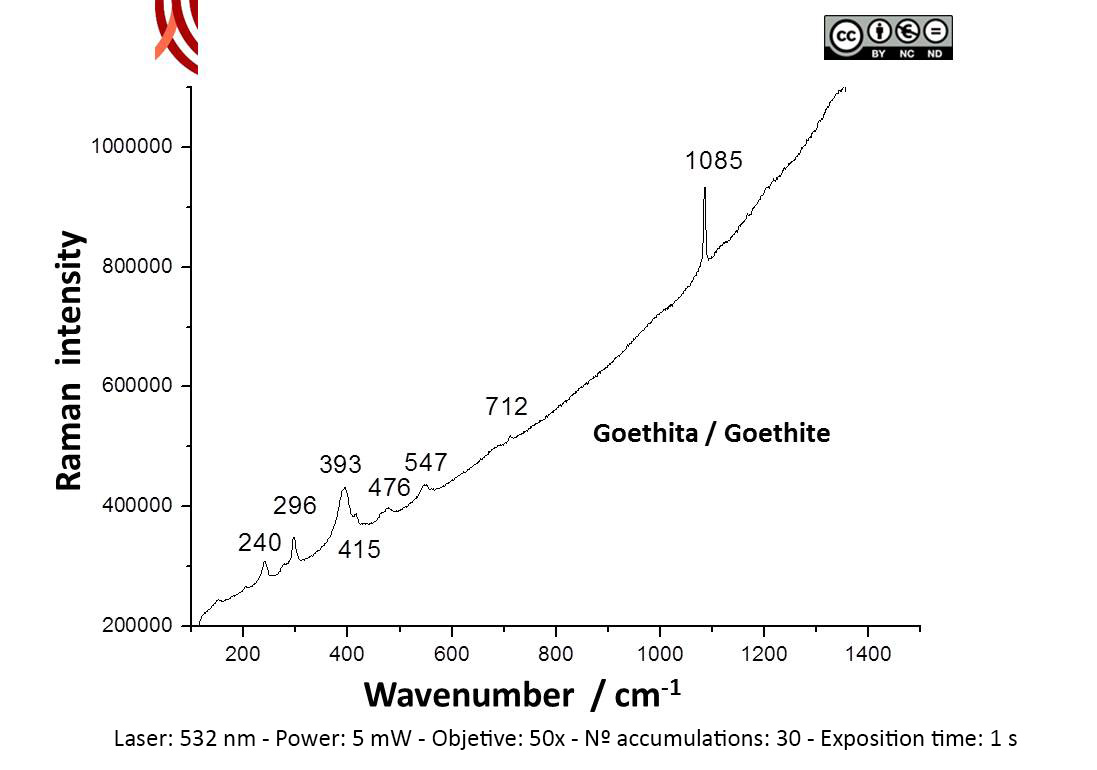
Archaeometric analysis Physical-chemical analysis Wall painting. Decoration analysis.
| |
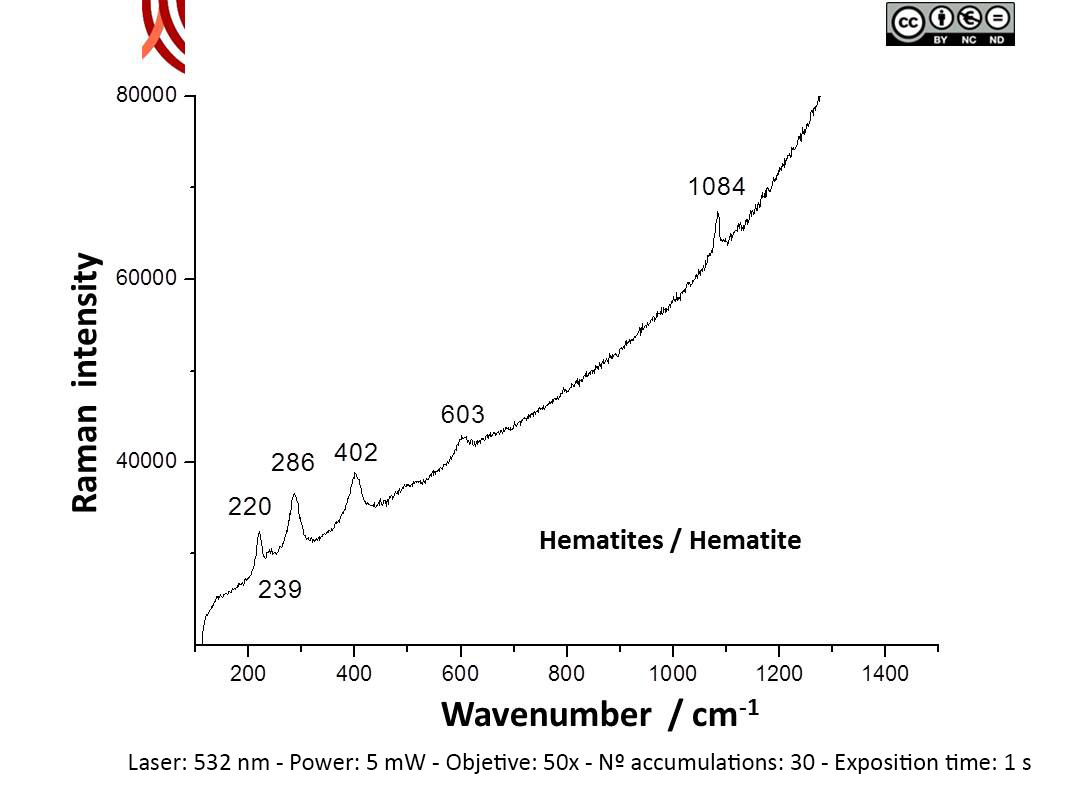
Raman Microscopy Mineral analysis Non destructive. Surface cleaning. Sample pretreatment is not required. Direct measurement. Micro-Raman Spectroscopy (MRS) Renishaw ‘in via’ Qontor Spectrometer coupled with a confocal Leica DM LM microscope (SCAI, University of Málaga), equipped with a solid state laser (473 nm, 25 mW), a Nd:YAG laser (532 nm, 50 mW) and a diode laser (785 nm, 300 mW), and a Peltier-cooled CCD detector, calibrated to the 520.5 cm-1 line of silicon. | |
X-Ray Fluorescence Elemental analysis Non destructive. Surface cleaning. Sample pretreatment is not required. Direct measurement. Energy dispersive X-ray fluorescence (EDXRF) An energy dispersive X-ray microfluorescence spectrometer (M4 Tornado, Bruker) (CICT, University of Jaen). This spectrometer is equipped with a microfocus X-ray tube with an Rh anode, a polycapillary lens for X-ray focussing, and a 30-mm2 energy dispersive detector (SDD). The sample chamber incorporates an XYZ motorized stage for sample positioning. A high resolution microscope is used to position the sample on the desired distance from the polycapillary. To increase the sensitivity of the low Z elements, the sample chamber can be brought under vacuum. For the analysis of the samples, a spot size of 25 μm was chosen at an operating X-ray tube voltage of 50 kV and intensity of 600 μA. The tube current was adapted for each sample in order to optimise the detection of X-rays. |















