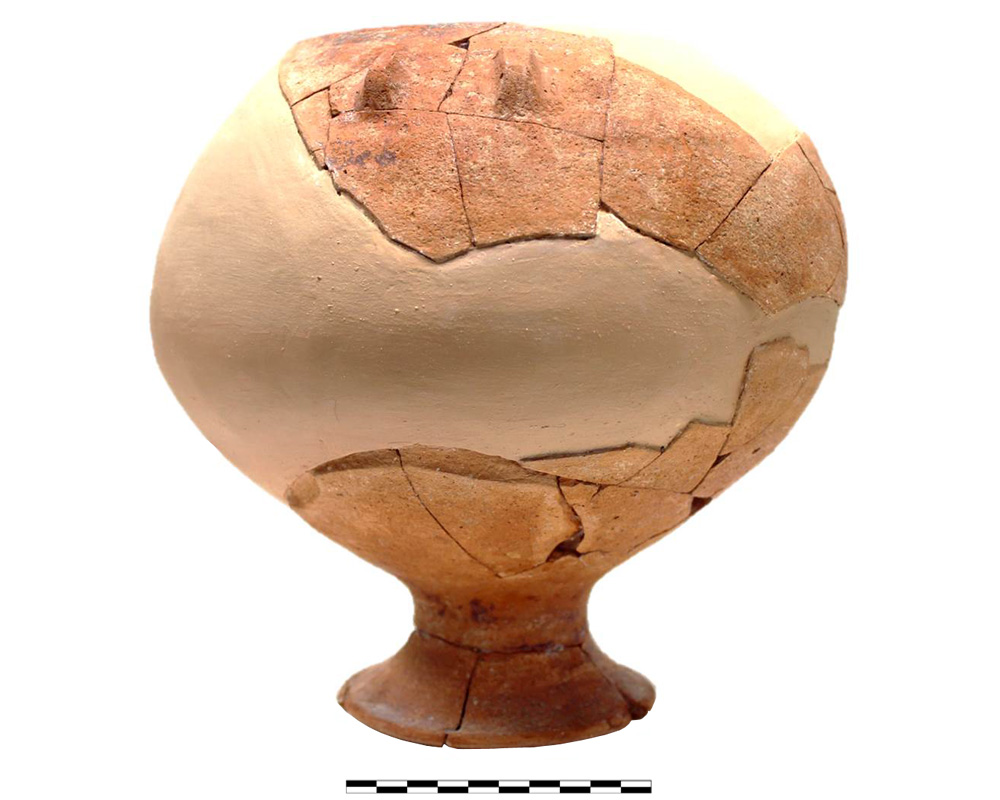
Ceramic vessel 1018. Cemetery Cerro de los Vientos (Baeza, Jaén, Spain)
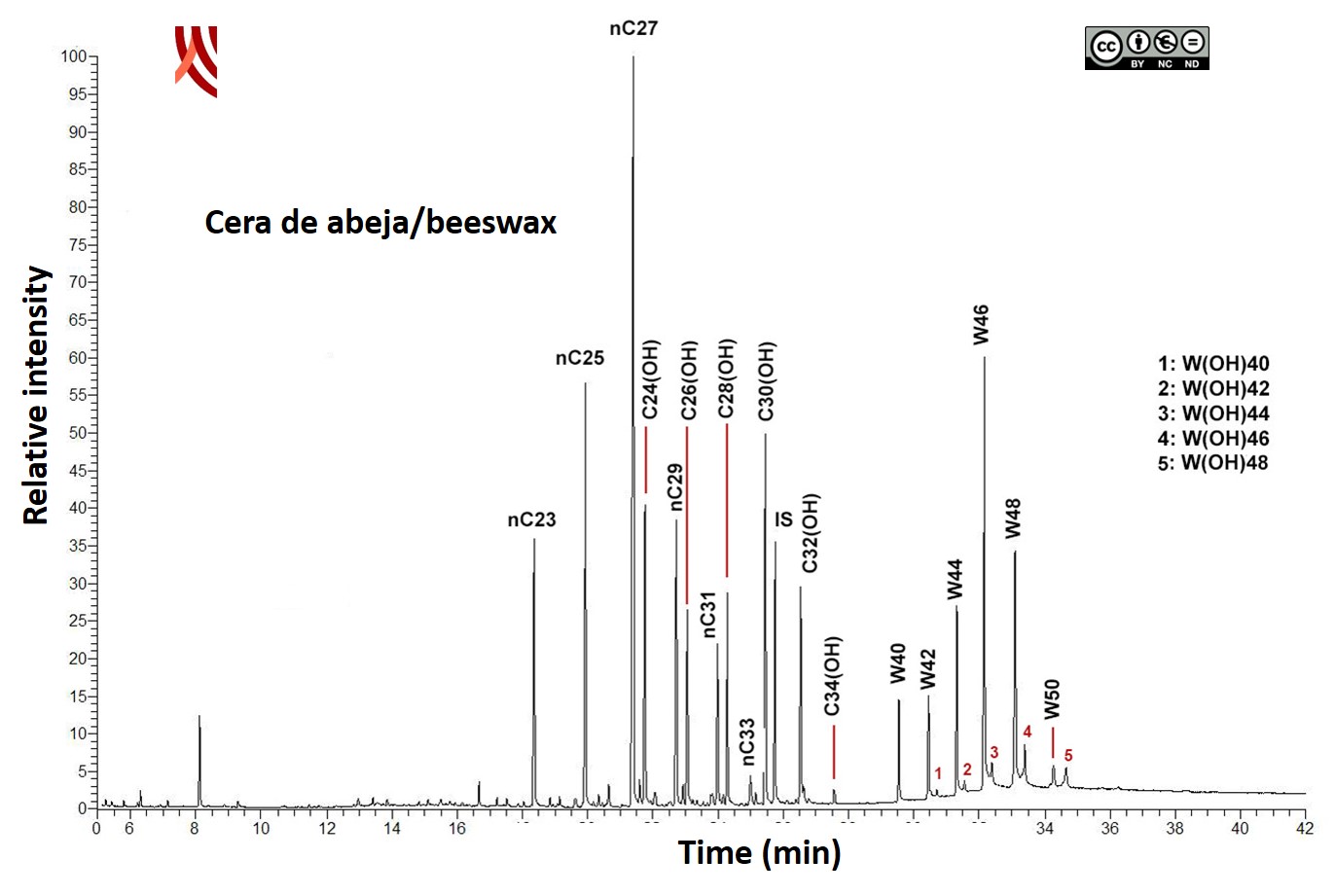
Content analysis using GC-MS identified the presence of beeswax markers: alkanes nC23 to nC33, long chain alcohols C24 (OH) to C34 (OH), palmitic acid wax esters W40-W50 and hydroxymonosters W (OH)40–W(OH)48.
Dimensions
Materials
pottery
Temporal
: Orientalising
: 8th-7th ct. BC
Spatial
: Cerro de los Vientos
: Puente del Obispo (Baeza, Jaén, Spain)
: WGS84
Copyrights
Creative Commons - Attribution, Non-Commercial, No Derivatives (BY-NC-ND)
References
Lechuga, M.A., Soto, M., (2017): "La tumba de la mujer y el joven del Cerro de los Vientos (Puente del Obispo, Baeza)", en Ruiz, A. y Molinos, M. (Eds.): Catálogo de la exposición La Dama, el Príncipe, el Héroe y la Diosa. Conserjería de Cultura de la Junta de Andalucía, Sevilla, pp. 109-117.
Digital Resources
-
 Instituto Universitario de Investigación en Arqueología Ibérica
Instituto Universitario de Investigación en Arqueología Ibérica Creative Commons - Attribution, Non-Commercial, No Derivatives (BY-NC-ND)
Arquiberlab
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/ -
 Instituto Universitario de Investigación en Arqueología Ibérica
Instituto Universitario de Investigación en Arqueología Ibérica Creative Commons - Attribution, Non-Commercial, No Derivatives (BY-NC-ND)
Arquiberlab
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/ - Instituto Universitario de Investigación en Arqueología Ibérica
Creative Commons - Attribution, Non-Commercial, No Derivatives (BY-NC-ND)
Arquiberlab
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/ -
 Instituto Universitario de Investigación en Arqueología Ibérica
Instituto Universitario de Investigación en Arqueología Ibérica Creative Commons - Attribution, Non-Commercial, No Derivatives (BY-NC-ND)
Arquiberlab
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/ -
 Instituto Universitario de Investigación en Arqueología Ibérica
Instituto Universitario de Investigación en Arqueología Ibérica Creative Commons - Attribution, Non-Commercial, No Derivatives (BY-NC-ND)
Arquiberlab
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/
Activities
Archaeometric analysis Spectroscopic and chromatographic analysis Pottery. Analysis of decoration and contents
| |
Raman Microscopy Mineral analysis of the red decoration Non destructive. Surface cleaning. Sample pretreatment is not required. Direct measurement MRS Renishaw ‘in via’ Reflex Spectrometer coupled with a confocal Leica DM LM microscope (CICT, University of Jaén), equipped with an argon ion laser (514.5 nm, 25 mW), diode laser (785 nm, 300 mW), Peltier-cooled CCD detector, and calibrated to the 520.5 cm-1 line of silicon | |
X-Ray Fluorescence Elemental analysis of the red decoration Non destructive. Surface cleaning. Sample pretreatment is not required. Direct measurement Energy dispersive X- ray fluorescence (EDXRF) An energy dispersive X-ray microfluorescence spectrometer (M4 Tornado, Bruker) was used for this paper (CICT, University of Jaen). This spectrometer is equipped with a microfocus X-ray tube with an Rh anode, a polycapillary lens for X-ray focussing, and a 30-mm2 energy dispersive detector (SDD). The sample chamber incorporates an XYZ motorized stage for sample positioning. A high resolution microscope is used to position the sample on the desired distance from the polycapillary. To increase the sensitivity of the low Z elements, the sample chamber can be brought under vacuum. For the analysis of the samples, a spot size of 25 μm was chosen at an operating X-ray tube voltage of 50 kV and intensity of 600 μA. The tube current was adapted for each sample in order to optimise the detection of X-rays | |
Gass Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Content analysis. Lipids Destructive method for the identification of the total lipid profile: fatty acids, sterols, wax esters, fatty alcohols, triacylglycerols, etc. Any remains of soil were removed with an electric hand-drill. The sample was then grinded to the appropriate size in an agatha mortar (0.25 mm). Extraction with a mixture chloroform/methanol (CHCl3:MeOH) (2:1 v/v) assisted by ultrasound. Derivatization of lipids to trimethylsilyl derivatives (TMS). The reaction takes place at 70 ° C for 30 min using N,O-bis- (trimethylsilyl) trifluoroacetamide (BSTFA), with 1% trimethylchlorosilane (TMCS). The sample is solved in cyclohexane and then injected in GC-MS. Chromatographic separation is performed applying a adequate temperature program GC-MS The analyses were performed using a using a gas chromatography equipment (model Thermo TraceGC Ultra) coupled to a Thermo DC Q II mass spectrometer. Autosampler Thermo Triplus (CICT, University of Jaén). The samples were introduced by on-column injection into a 15 m x 0.25 mm I.D. fused silica capillary column, coated with poly(dimethylsiloxane) stationary phase with 0.1 μm film thickness. Helium was used as the carrier gas (purity 99.99%) |












