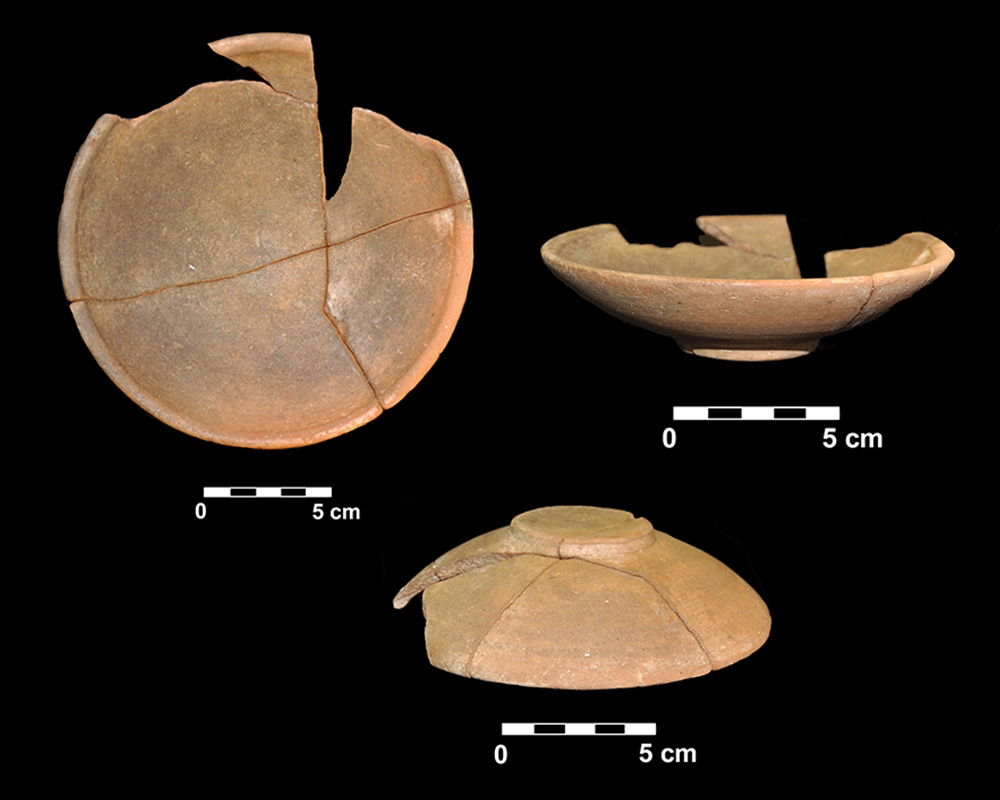
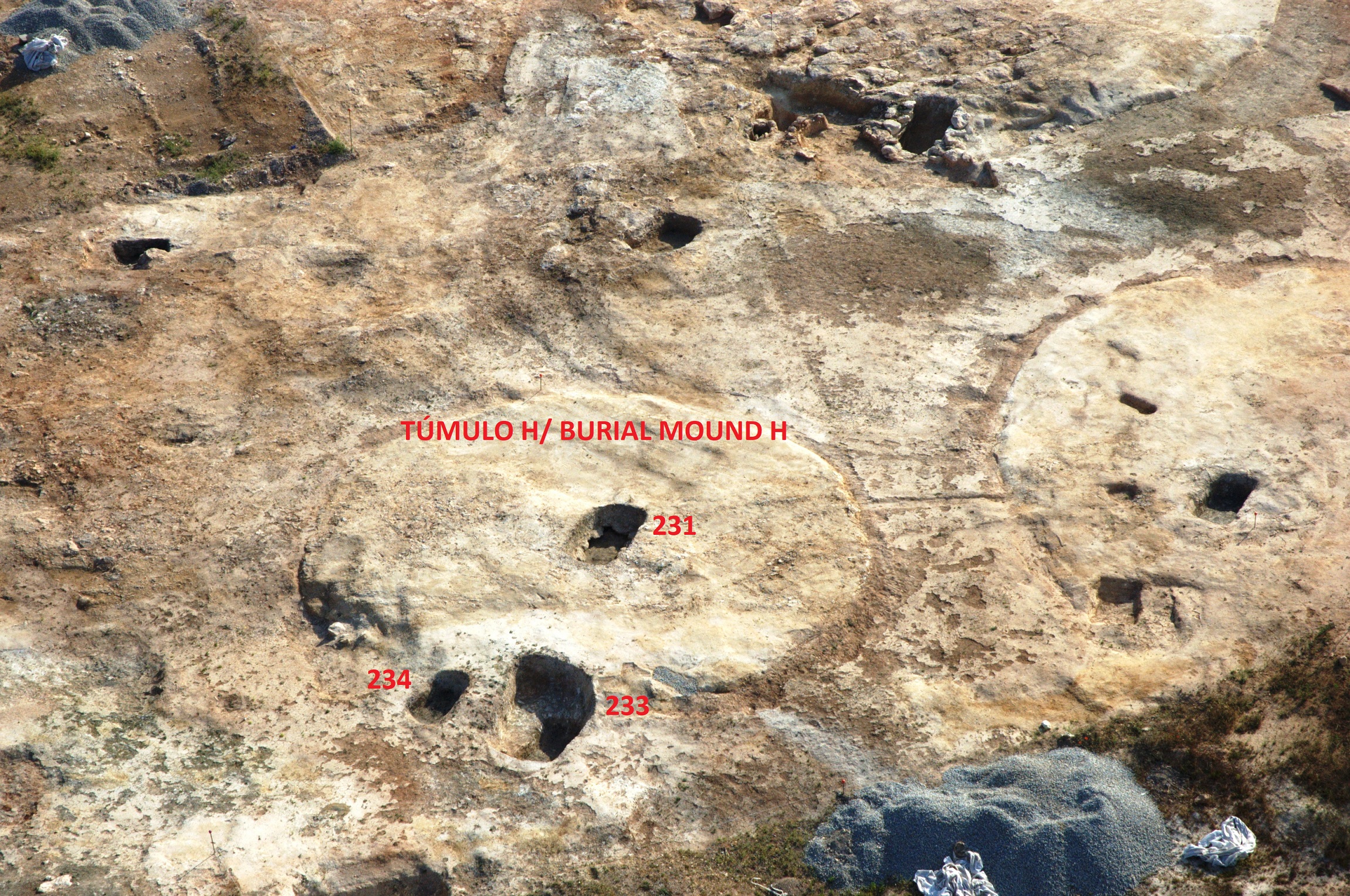
Ceramic vessel 139. Grave 231. Cemetery of La Noria (Fuente de Piedra, Málaga, Spain)
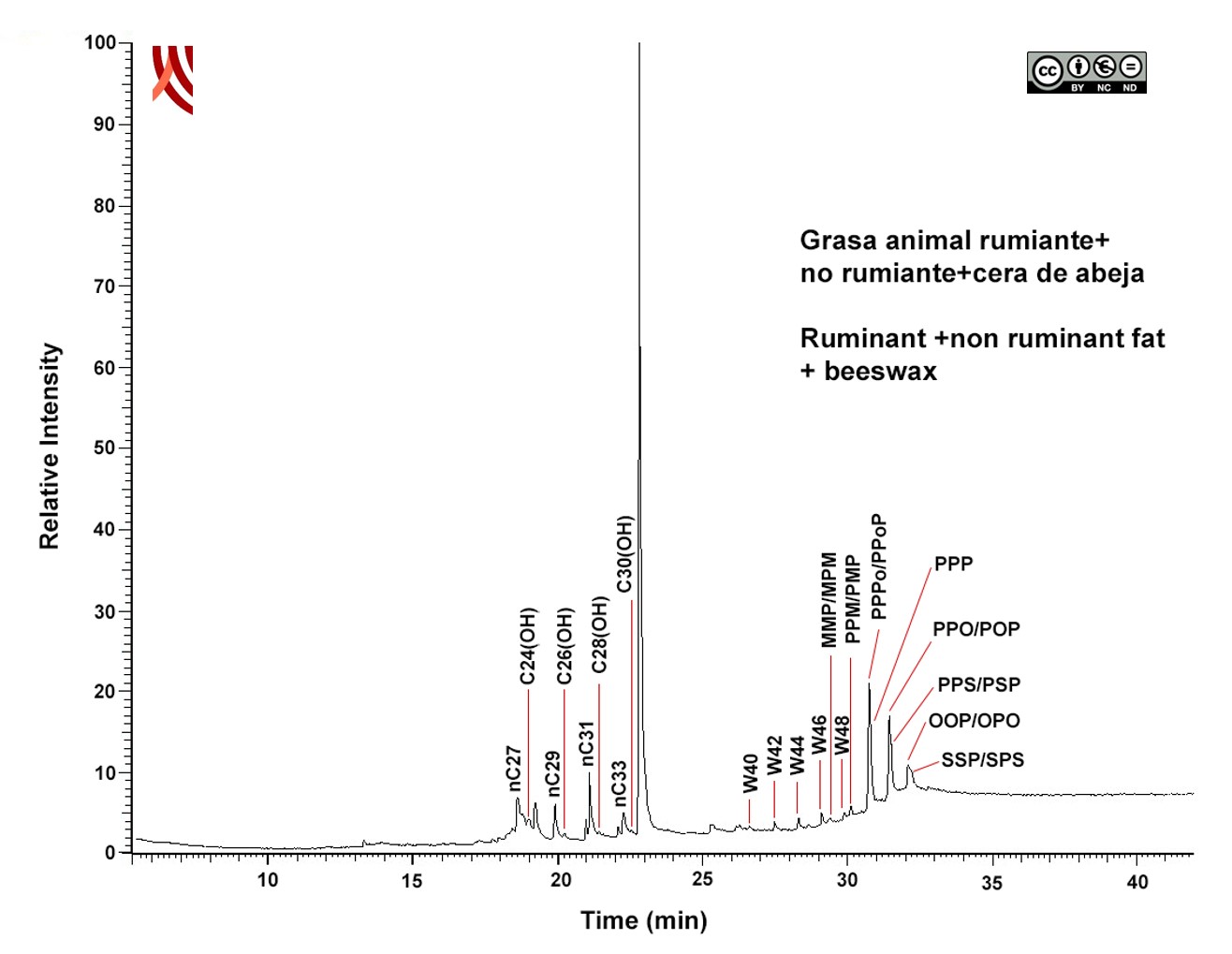
The chemical markres of beeswax identified are: odd-chain alkanes (nC27-nC31), fatty alcohols [C24 (OH) -C30 (OH)] and esters of palmitic acid waxes (W40 -W48).
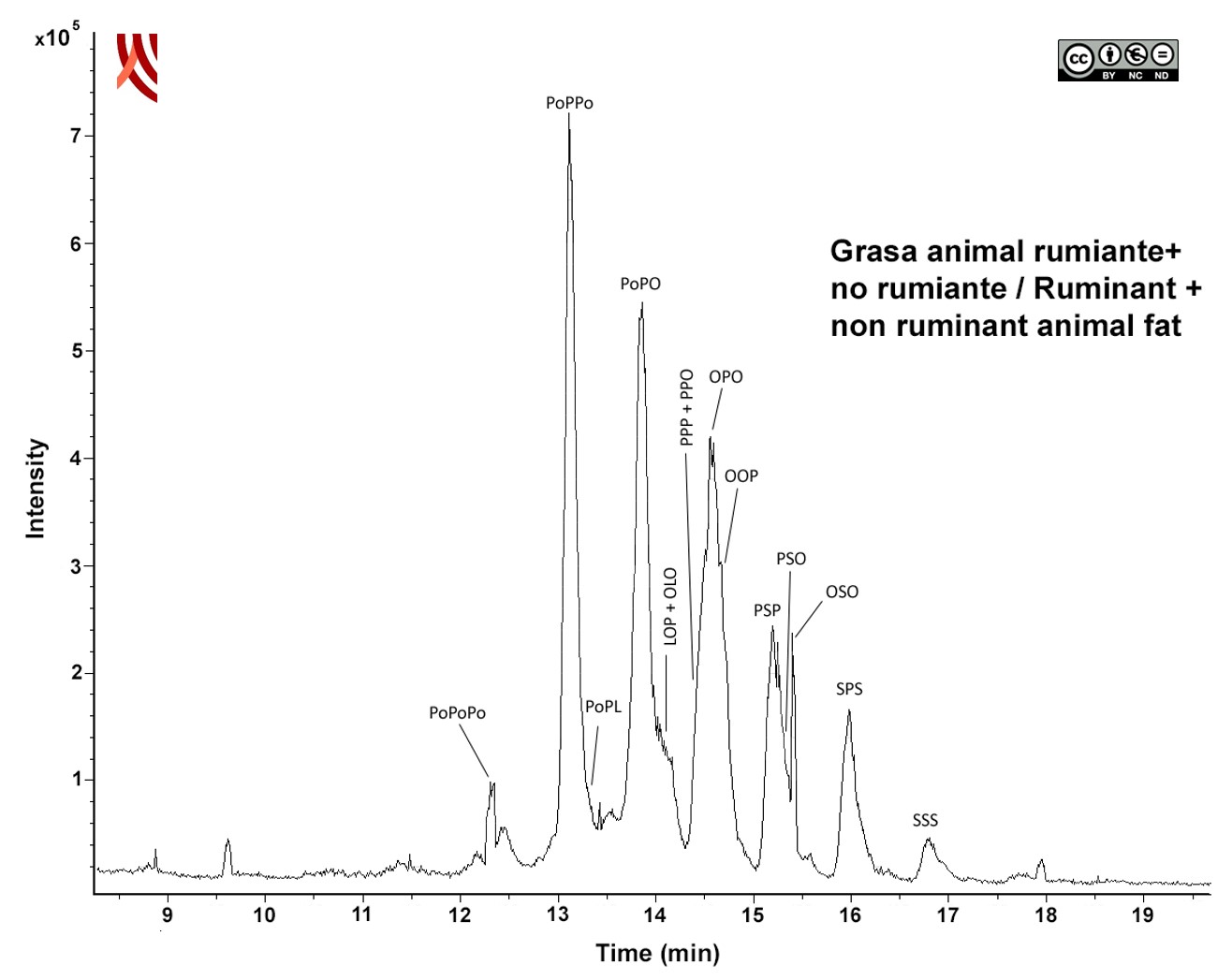
In the case of animal fat, the profile of TAGs obtained by HPLC-APCI-MS shows the presence of a mixture of ruminant fat (highly saturated TAGs SSP, PPS, SSS), with non-ruminant (abundant TAGs, formed mainly by oleic and palmitic acids PPO, OOP, PPP, with a higher concentration of the latter compared to ruminant fat). The study by HPLC-APCI-MS determines a P/S ratio in sn-2 position of 73/27. This intermediate value would confirm the mix of both types of fats.
Dimensions
: 4 Centimeters
: 16 Centimeters
Materials
pottery
Temporal
: Iberians, Iberian
: Late 6th ct. BC-early 5th ct. BC
Spatial
: Cemetery of La Noria
: Fuente de Piedra (Málaga, Spain)
: WGS84
Copyrights
Creative Commons - Attribution, Non-Commercial, No Derivatives (BY-NC-ND)
References
Ruiz, A., Molinos, M., Cano, M.F., Montes, E., Ortuño, E. (2017): "El túmulo C de la necrópolis de la Noria (Fuente de Piedra). ¿La tumba de dos mujeres?", en: Ruiz, A. y Molinos, M. (Eds.), Catálogo de la exposición La Dama, el Príncipe, el Héroe y la Diosa. Conserjería de Cultura de la Junta de Andalucía, Sevilla, pp. 119-128.
Digital Resources
-
 Instituto Universitario de Investigación en Arqueología Ibérica
Instituto Universitario de Investigación en Arqueología Ibérica Creative Commons - Attribution, Non-Commercial, No Derivatives (BY-NC-ND)
Arquiberlab
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/ -
 Instituto Universitario de Investigación en Arqueología Ibérica
Instituto Universitario de Investigación en Arqueología Ibérica Creative Commons - Attribution, Non-Commercial, No Derivatives (BY-NC-ND)
Arquiberlab
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/ -
 Instituto Universitario de Investigación en Arqueología Ibérica
Instituto Universitario de Investigación en Arqueología Ibérica Creative Commons - Attribution, Non-Commercial, No Derivatives (BY-NC-ND)
Arquiberlab
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/ -
 Instituto Universitario de Investigación en Arqueología Ibérica
Instituto Universitario de Investigación en Arqueología Ibérica Creative Commons - Attribution, Non-Commercial, No Derivatives (BY-NC-ND)
Arquiberlab
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/ -
 Instituto Universitario de Investigación en Arqueología Ibérica
Instituto Universitario de Investigación en Arqueología Ibérica Creative Commons - Attribution, Non-Commercial, No Derivatives (BY-NC-ND)
Arquiberlab
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/
Activities
Archaeometric analysis Physical-chemical analysis Chromatographic analysis and structural determination
| |
Gass Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Pottery. Contents analysis Destructive method for the identification of the total lipid profile: fatty acids, sterols, wax esters, fatty alcohols, triacylglycerols, etc. . Any remains of soil were removed with an electric hand-drill. The sample was then grinded to the appropriate size in an agatha mortar (0.25 mm). Extraction with a mixture chloroform/methanol (CHCl3:MeOH) (2:1 v/v) assisted by ultrasound. Derivatization of lipids to trimethylsilyl derivatives (TMS). The reaction takes place at 70 ° C for 30 min using N,O-bis- (trimethylsilyl) trifluoroacetamide (BSTFA), with 1% trimethylchlorosilane (TMCS). The sample is solved in cyclohexane and then injected in GC-MS. Chromatographic separation is performed applying a adequate temperature program. Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Gas chromatograph Thermo TraceGC Ultra coupled to a Thermo DC Q II mass spectrometer. Autosampler Thermo Triplus (CICT, University of Jaén) and equipped with a 15 m x 0.25 mm I.D. fused silica capillary column, coated with poly(dimethylsiloxane) stationary phase with 0.1 μm film thickness. Helium (He) is used as the carrier gas. | |
High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Pottery. Contents analysis Destructive method for the identification of TAGs content. Any remains of soil were removed with an electric hand-drill. The sample was then grinded to the appropriate size in an agatha mortar (0.25 mm). Extraction with a mixture chloroform/methanol (CHCl3:MeOH) (2:1 v/v) assisted by ultrasound. Derivatization is no needed. Lipid extract is solved in isopropanol and then injected in HPLC-APCI-MS. Chromatographic separation is performed applying a adequate mobile phase gradient (mixture of isopropanol and methanol). High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization-Mass Spectrometry (HPLC-APCI-MS) Agilent 1290 Infinity HPLC system connected to an Agilent 6220 TOF (time-of-flight) mass spectrometer equipped with APCI (Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization) interface. (Departement of Physical and Analytical Chemistry, University of Jaén). Chromatographic column Zorbax Eclipse Plus C18 (150 mm x 4.6 mm, 1.8 μm particle size) |
































