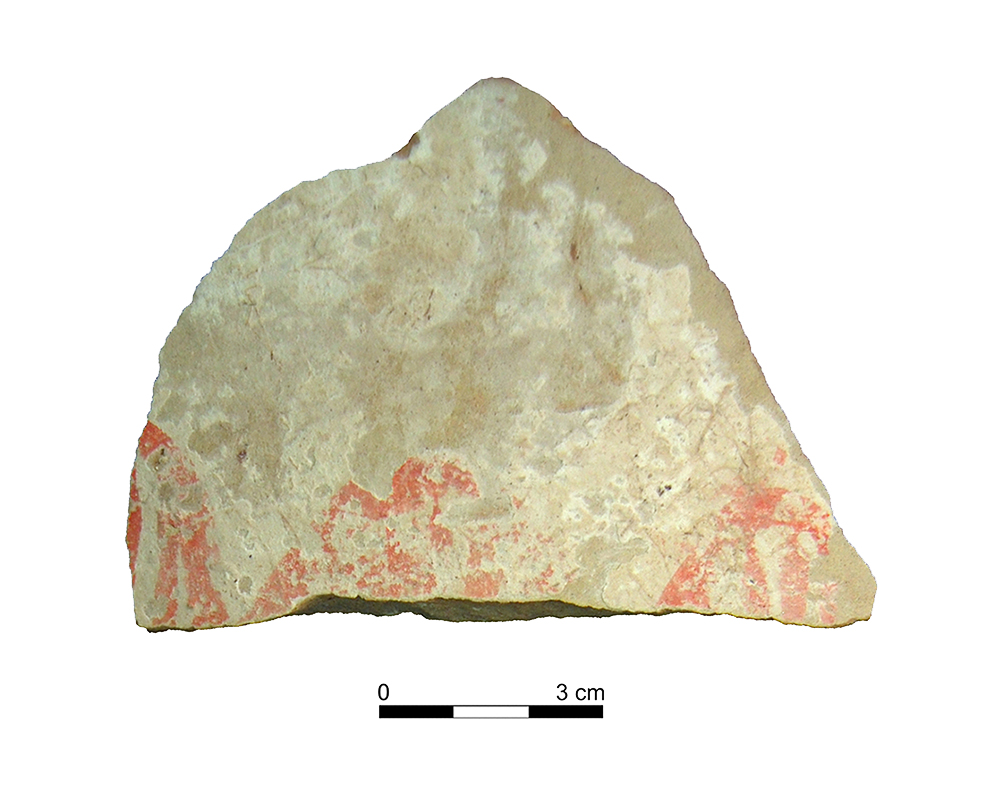
Ceramic vessel 34004-2. Burial mound 34. cemetery of Tútugi.
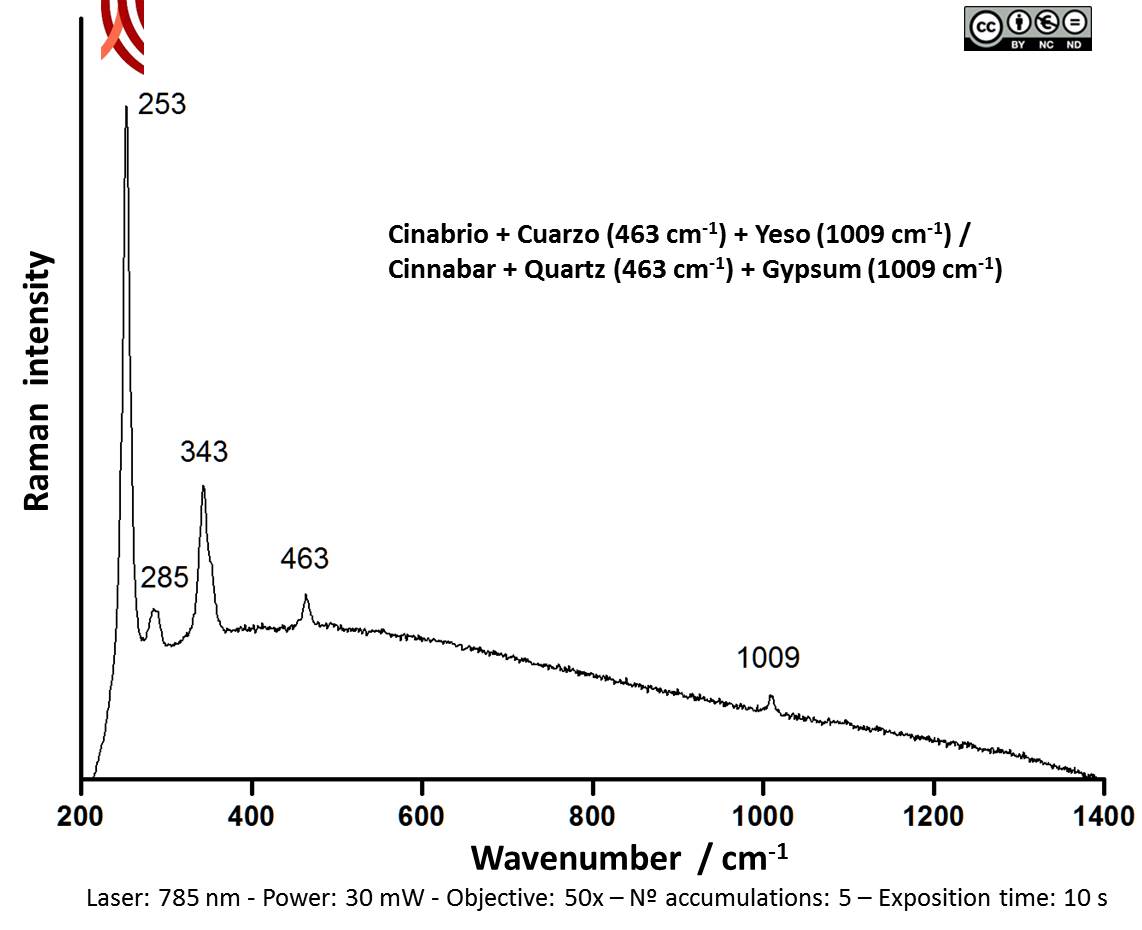
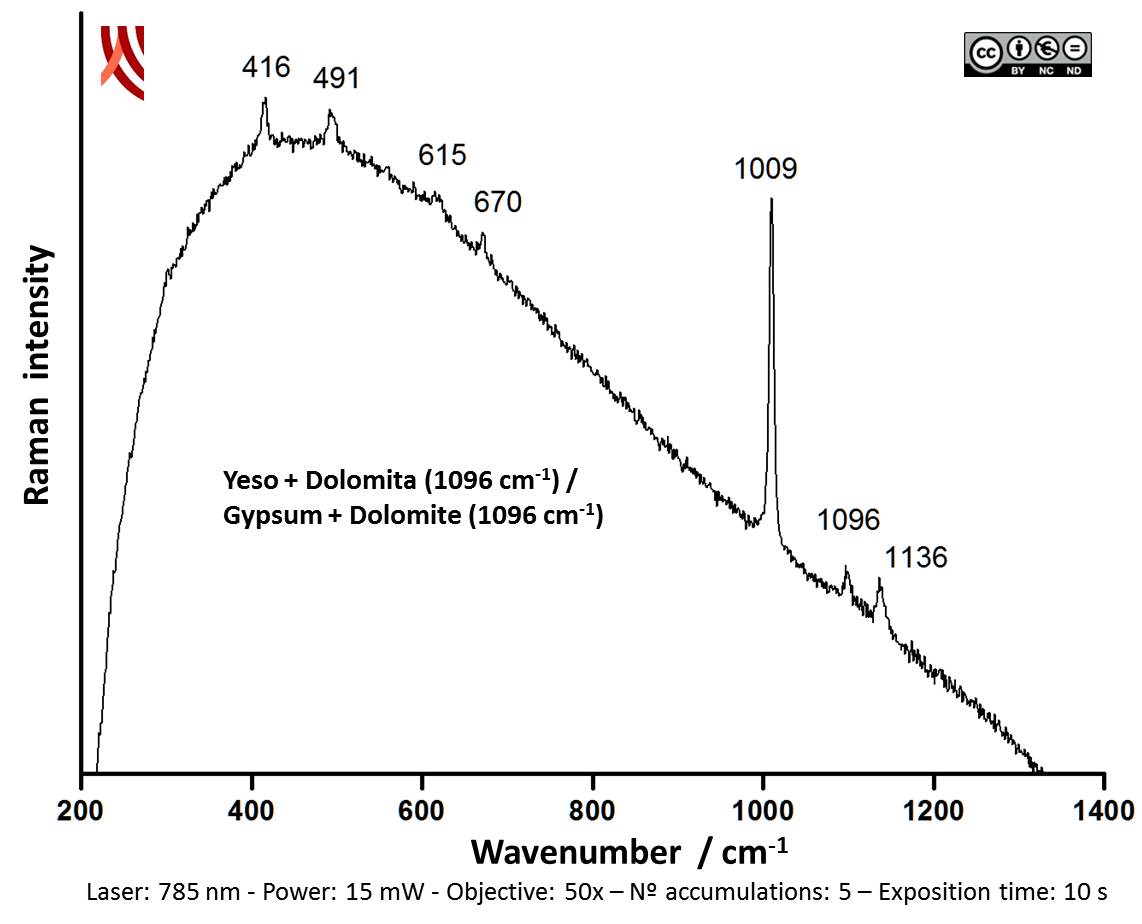
Cinnabar is known to have been used in the Iberian Peninsula in megalithic contexts and for the decoration of Iberian sculptures of a highly symbolic value such as the Lady of Baza and the Lady of Elche. The case under study here confirm that cinnabar was also used for decoration of the ceramic vessels of grave goods, which is further evidence of its exclusiveness.
Dimensions
: 9 Centimeters
: 7 Centimeters
Materials
pottery
Temporal
: Iberians, Iberian
: Late 5th ct. BC-early 4th ct. BC
Spatial
: Cemetery of Tutugi
: Galera, Granada, Spain
: WGS84
Copyrights
Creative Commons - Attribution, Non-Commercial, No Derivatives (BY-NC-ND)
References
Rodríguez Ariza, Mª O. (2014): La necrópolis ibérica de Tútugi (2000-2012). CAAItextos. Universidad de Jaén, Jaén.
Sánchez, A.; Parras, D.; Tuñón, J. A. Y Ramos, N. (2014): “Análisis de recubrimientos y pigmentos en la necrópolis ibérica de Tútugi (Galera, Granada)”, Mª O. Rodríguez (ed): La necrópolis ibérica de Tútugi (2000-2012). Universidad de Jaén e Instituto Universitario de Investigación en Arqueología Ibérica, Jaén. 349-368.
Digital Resources
-

Creative Commons - Attribution, Non-Commercial, No Derivatives (BY-NC-ND)
Arquiberlab
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/ -
 Instituto Universitario de Investigación en Arqueología Ibérica
Instituto Universitario de Investigación en Arqueología Ibérica Creative Commons - Attribution, Non-Commercial, No Derivatives (BY-NC-ND)
Arquiberlab
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/ -
 Instituto Universitario de Investigación en Arqueología Ibérica
Instituto Universitario de Investigación en Arqueología Ibérica Creative Commons - Attribution, Non-Commercial, No Derivatives (BY-NC-ND)
Arquiberlab
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/ - Instituto Universitario de Investigación en Arqueología Ibérica
pdf file
Creative Commons - Attribution, Non-Commercial, No Derivatives (BY-NC-ND)
Arquiberlab
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/ -

Creative Commons - Attribution, Non-Commercial, No Derivatives (BY-NC-ND)
Arquiberlab
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/
Activities
Archaeometric analysis Physical-chemical analysis Ceramic. Analysis of decoration.
| |
Spectroscopic analysis Mineral analysis of red decoration and white layer Non destructive. Surface cleaning. Sample pretreatment is not required. Direct measurement. Micro-Raman Spectroscopy (MRS) Renishaw ‘in via’ Reflex Spectrometer coupled with a confocal Leica DM LM microscope (CICT, University of Jaén), equipped with a diode laser (785 nm, 300 mW), and a Peltier-cooled CCD detector, calibrated to the 520.5 cm-1 line of silicon. | |
X-Ray Fluorescence Elemental analysis of red decoration and white layer Non destructive. Surface cleaning. Sample pretreatment is not required. Direct measurement. Energy dispersive X- ray fluorescence (EDXRF) EDAX (model Eagle III) fluorescence spectrometer (CITI, University of Seville). This spectrometer is equipped with a microfocus X-ray tube with an Rh anode, a polycapillary lens for X-ray focussing, and an 80 mm2 energy dispersive Si-(Li) detector. The sample chamber incorporates an XYZ motorized stage for sample positioning. A high resolution microscope is used to position the sample on the desired distance from the polycapillary. To increase the sensitivity of the low Z elements, the sample chamber can be brought under vacuum. For the analysis of the samples, a spot size of 300 µm was chosen at an operating X-ray tube voltage of 40 kV. The tube current was adapted for each sample in order to optimise the detection of X-rays. |
































