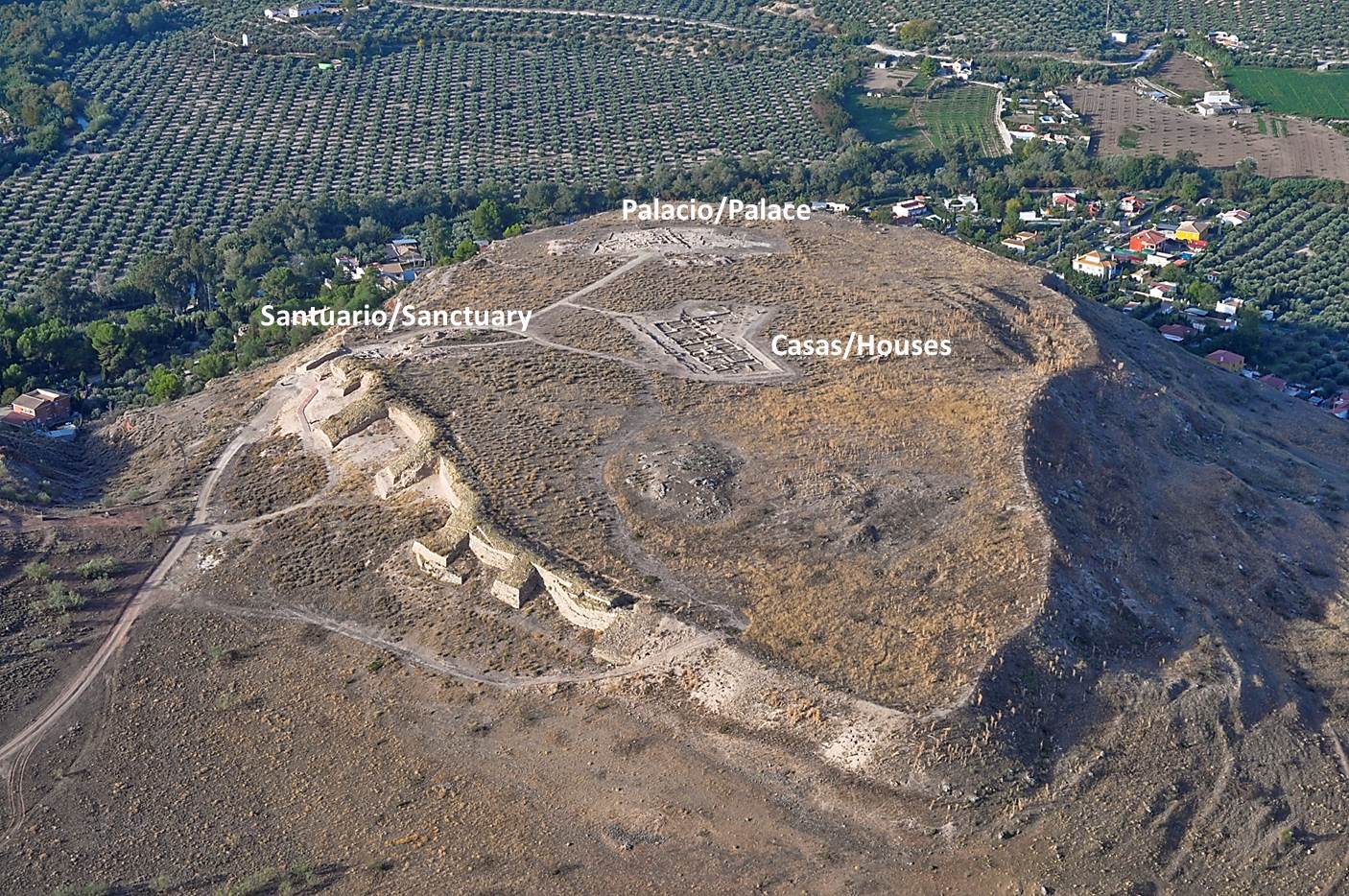
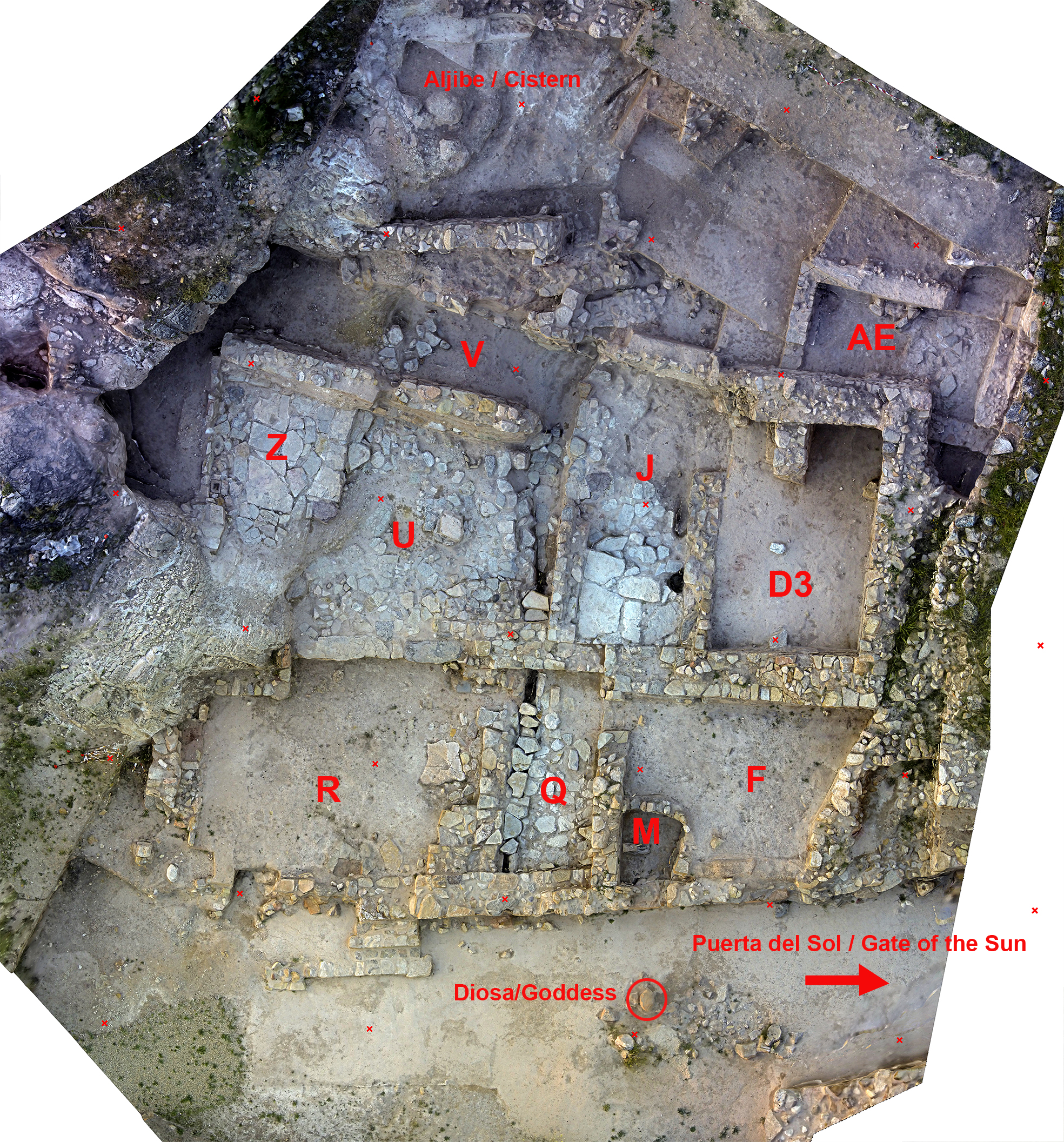
Covering F-2. Oppidum Puente Tablas
Dimensions
Materials
covering
Temporal
: Iberians, Iberian
: Early 4th BC
Spatial
: Oppidum de Puente Tablas
: Jaén, Spain
: WGS84
Copyrights
Creative Commons - Attribution, Non-Commercial, No Derivatives (BY-NC-ND)
References
Ruiz A. y M. Molinos (coord.) (2015): Jaén, tierra ibera. 40 años de investigación y transferencia. Universidad de Jaén.
Digital Resources
-

Creative Commons - Attribution, Non-Commercial, No Derivatives (BY-NC-ND)
Arquiberlab
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/ -

Creative Commons - Attribution, Non-Commercial, No Derivatives (BY-NC-ND)
Arquiberlab
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/ -

Creative Commons - Attribution, Non-Commercial, No Derivatives (BY-NC-ND)
Arquiberlab
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/ -
Creative Commons - Attribution, Non-Commercial, No Derivatives (BY-NC-ND)
Arquiberlab
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/ -
Creative Commons - Attribution, Non-Commercial, No Derivatives (BY-NC-ND)
Arquiberlab
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/ -
Creative Commons - Attribution, Non-Commercial, No Derivatives (BY-NC-ND)
Arquiberlab
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/ -
Information about the samples analysed is included
Creative Commons - Attribution, Non-Commercial, No Derivatives (BY-NC-ND)
Arquiberlab
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/
Activities
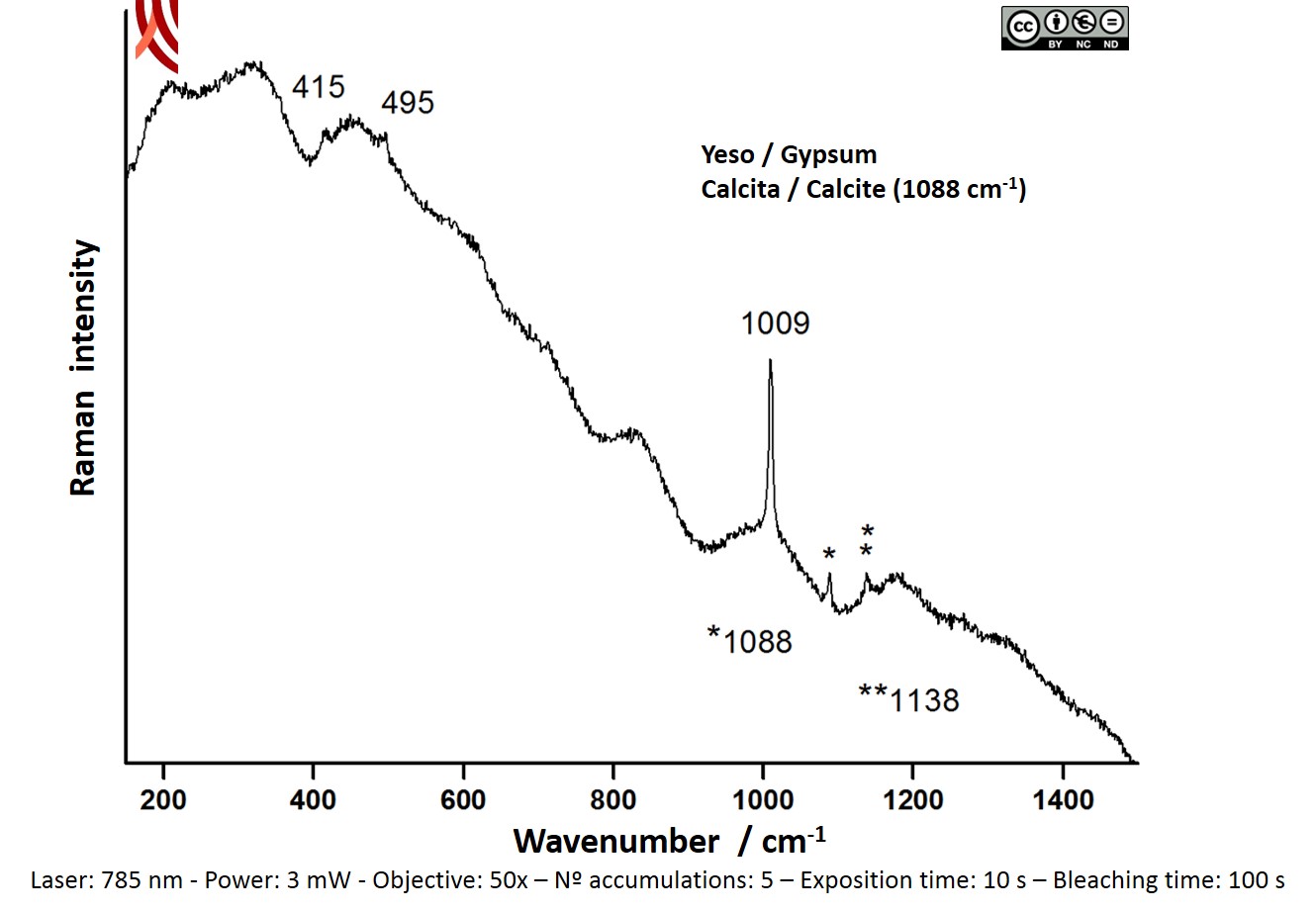
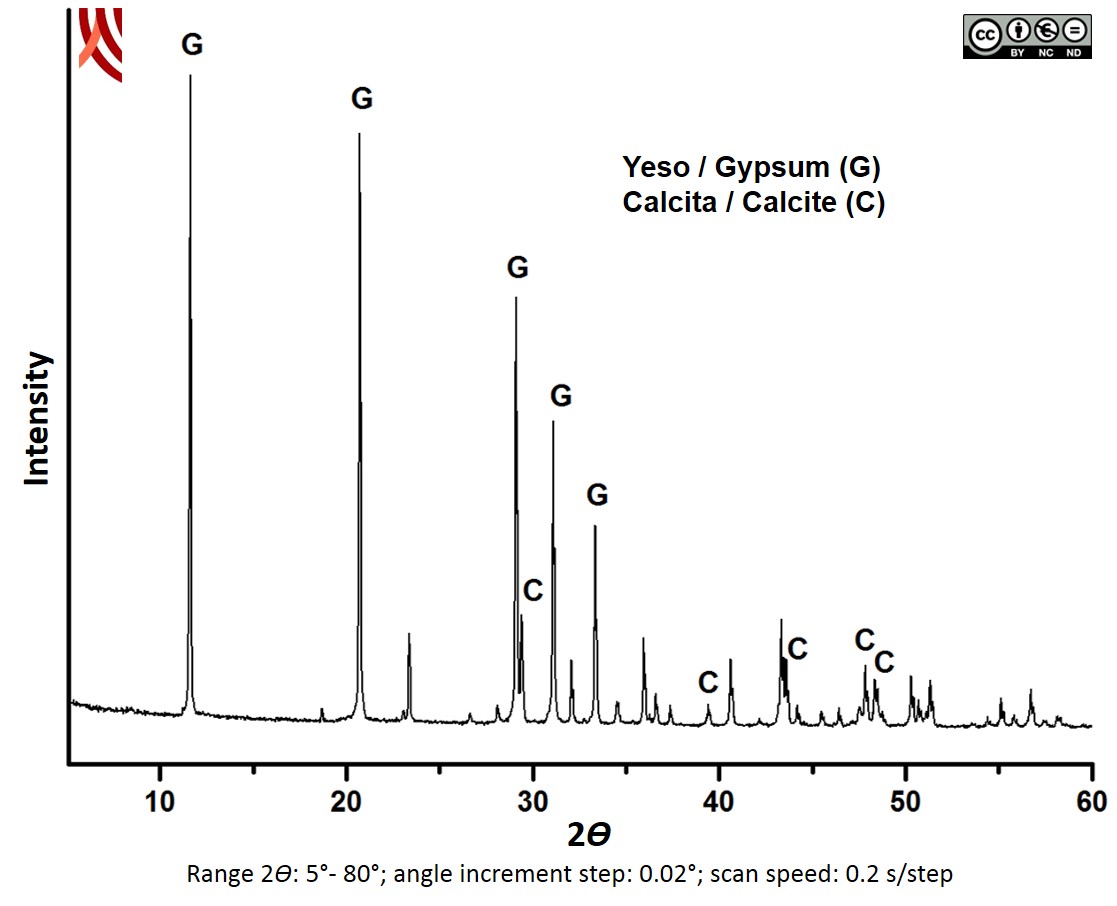
Archaeometric analysis Physical-chemical analysis Covering. Composition analysis
| |
Raman Microscopy Mineral analysis Non destructive. Surface cleaning. Sample pretreatment is not required. Direct measurement. Micro-Raman Spectroscopy (MRS) Renishaw ‘in via’ Reflex Spectrometer coupled with a confocal Leica DM LM microscope (CICT, University of Jaén), equipped with a diode laser (785 nm, 300 mW), and a Peltier-cooled CCD detector, calibrated to the 520.5 cm-1 line of silicon. | |
X-Ray Fluorescence Elemental analysis Recommended sample quantity is 0.1 g. The sample is mixed with wax (as binder) and boric acid. This mixture is processed in the form of pellet (10 mm diameter) with the aid of a hand press and placed in an isolated chamber where a vacuum (%3C10 Pa) is made. Wavelength Dispersive X-ray Fluorescence (WDXRF) AXIOS Panalytical wavelength dispersive X-ray fluorescence (WD-XRF) spectrometer owned by the Center for Innovation and Technological Research in the University of Seville (CITIUS) (Figure 12). The main features of the device include: Rh anode (4.4 kW maximum power), 3 collimators (150 μm, 300 μm and 700 μm), 6 analyzer crystals (LIF200, LIF 220, PX-10, Ge111, PE002, PX-1) that allow qualitative and quantitative chemical analysis of elements from O to U in a wide range of concentrations (from main components to traces), a flow detector (for Z%3C29 elements) and a scintillation detector (for Z>29 elements). | |
X-Ray Difraction Mineral analysis Method of crystalline powder. The samples were ground to powder in an Agatha mortar until an adequate particle size (0.25 mm) and weighed approximately 1 g. X-ray difracction (XRD) The analyses were carried out in the Scientific Instrument Service of the University of Granada using a diffractometer BRUKER D8 ADVANCE equipped with a copper tube, geometry θθ and with a LYNXEYE Detector. Diffraction data were collected in the range of 2θ Bragg angles from 5º to 80º in 0.02º steps, step time 0.2 s. Peaks were identified with the Software Package Xpowder Plus and with manuals of reference. |
































