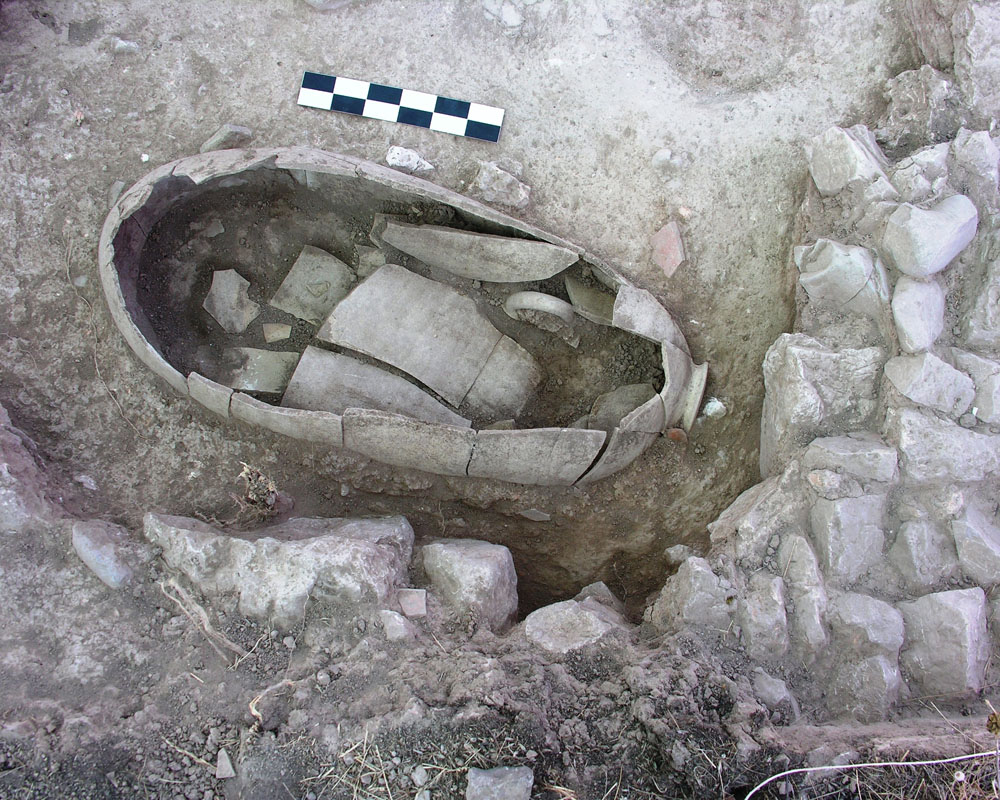
Amphora 10-Q. Oppidum of Puente Tablas (Jaén, Spain)
Dimensions
: 90 Centimeters
: 40 Centimeters
Materials
pottery
Temporal
: Iberian
: 3rd ct. BC
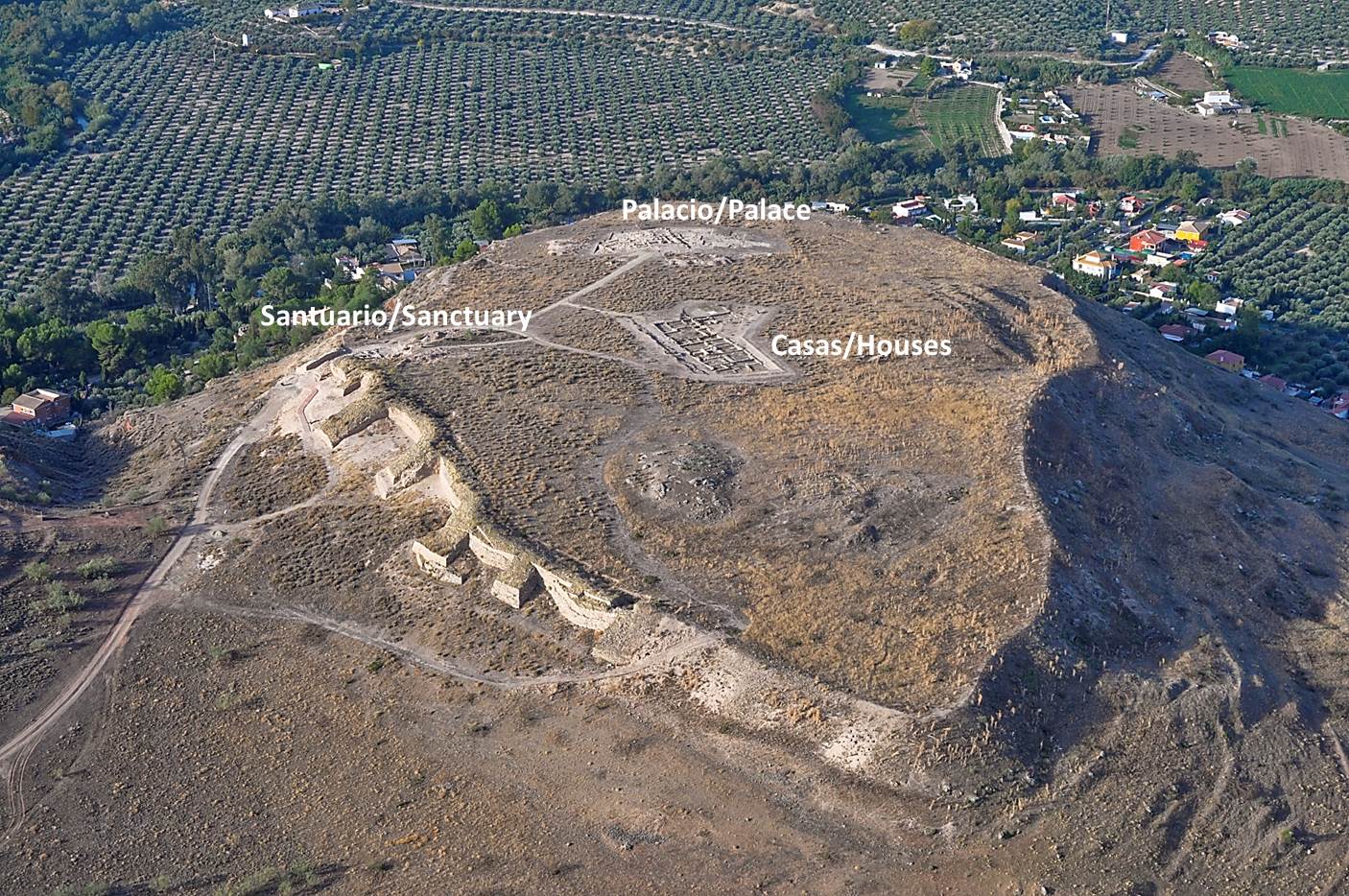
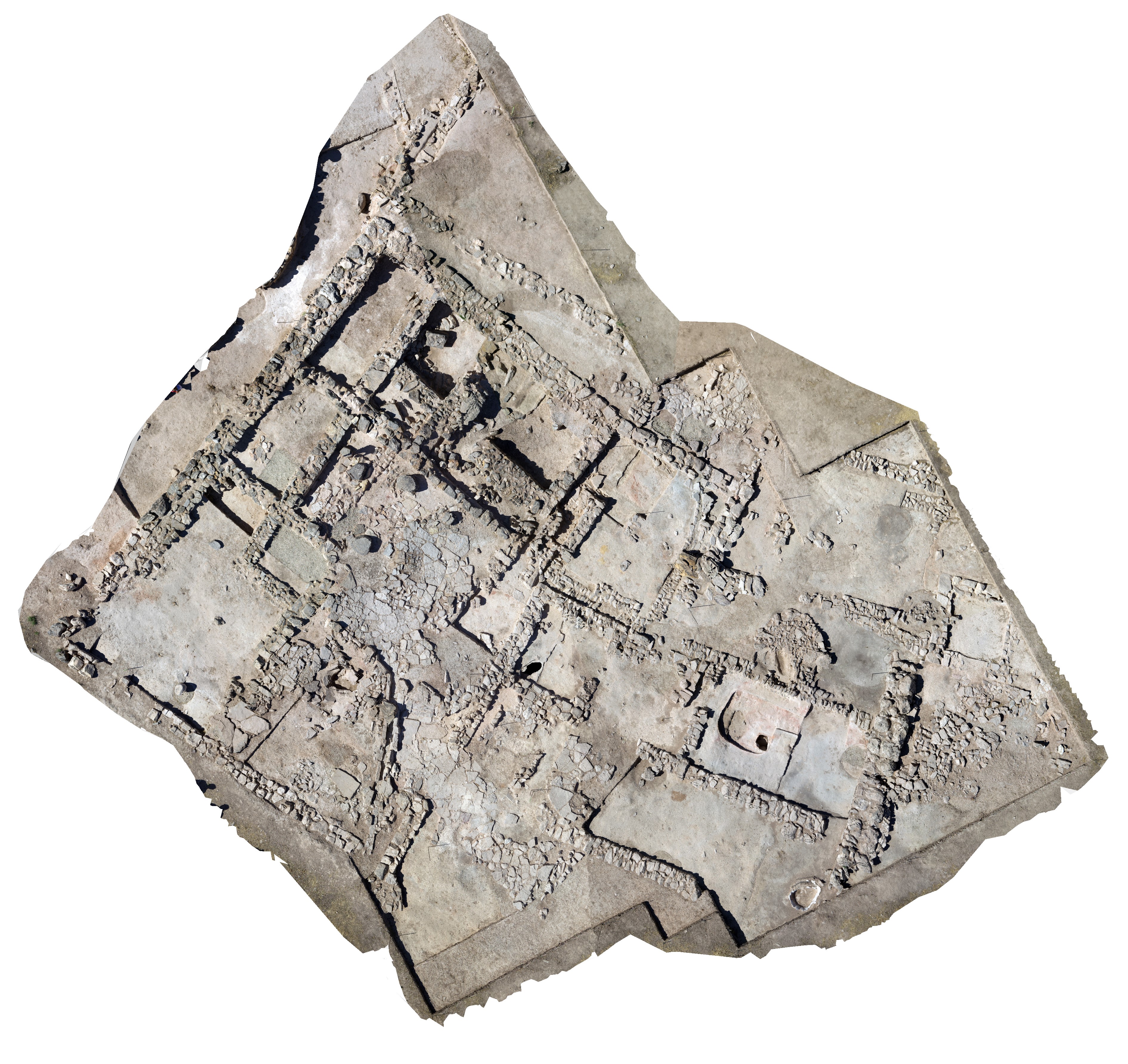
Spatial
: Oppidum de Puente Tablas
: Puente tablas, Jaén, Spain
: WGS84
Copyrights
Creative Commons - Attribution, Non-Commercial, No Derivatives (BY-NC-ND)
References
Ruiz, A., Molinos, M., Rueda, C. y Fernández, R. (2015):" El palacio y el urbanismo del oppidum de Puente Tablas", en A. Ruiz y M. Molinos: Jaén, tierra ibera 40 años de investigación y transferencia. Universidad de Jaén. Pp. 107-118.
Sánchez, A., Parras D. J., Tuñón, J.A., Rísquez, C., Rodríguez, Mª O. Montejo, M., Ramos, N., García, J. F. y Márquez, F. (2014): “Physical-chemical analysis for the research and the valorisation of the oppidum of Puente Tablas (Jaén, Spain)”, en M.A. Rogerio (ed.): Science, Technology and Cultural Heritage. Taylor %26 Francis Group. London. Pp. 103–108.
Digital Resources
-
 Instituto Universitario de Investigación en Arqueología Ibérica. Universidad de Jaén
Instituto Universitario de Investigación en Arqueología Ibérica. Universidad de Jaén Creative Commons - Attribution, Non-Commercial, No Derivatives (BY-NC-ND)
Arquiberlab
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/ -
 Instituto Universitario de Investigación en Arqueología Ibérica. Universidad de Jaén
Instituto Universitario de Investigación en Arqueología Ibérica. Universidad de Jaén Creative Commons - Attribution, Non-Commercial, No Derivatives (BY-NC-ND)
Arquiberlab
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/ -
 Instituto Universitario de Investigación en Arqueología Ibérica. Universidad de Jaén
Instituto Universitario de Investigación en Arqueología Ibérica. Universidad de Jaén Creative Commons - Attribution, Non-Commercial, No Derivatives (BY-NC-ND)
Arquiberlab
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/ -
 Instituto Universitario de Investigación en Arqueología Ibérica. Universidad de Jaén
Instituto Universitario de Investigación en Arqueología Ibérica. Universidad de Jaén Creative Commons - Attribution, Non-Commercial, No Derivatives (BY-NC-ND)
Arquiberlab
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/ -
 Instituto Universitario de Investigación en Arqueología Ibérica. Universidad de Jaén
Instituto Universitario de Investigación en Arqueología Ibérica. Universidad de Jaén Creative Commons - Attribution, Non-Commercial, No Derivatives (BY-NC-ND)
Arquiberlab
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/
Activities
Archaeometric analysis Chromatographic analysis and structural determination Pottery. Content analysis
| |
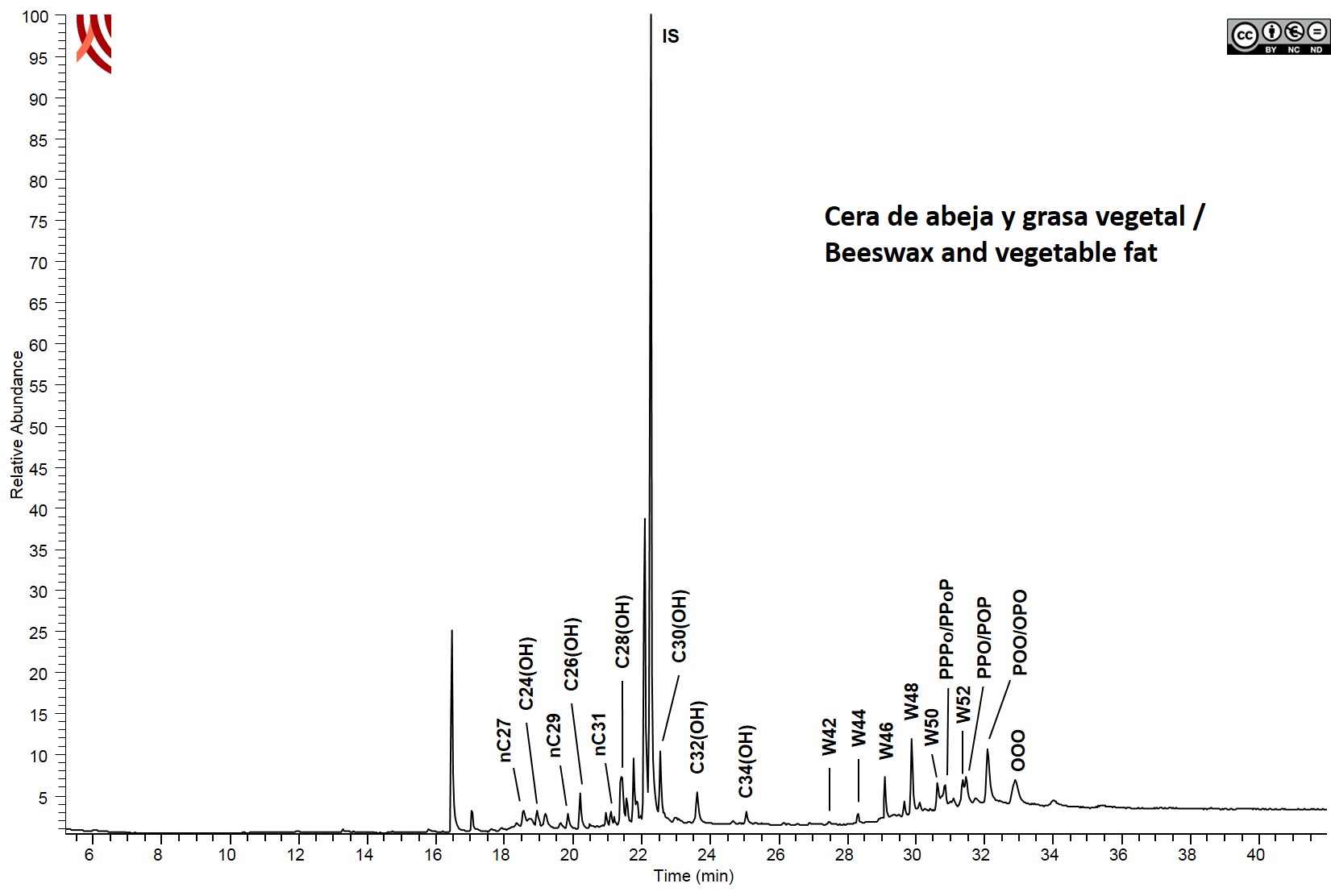
Gass Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Pottery. Lipids analysis Destructive method for the identification of the total lipid profile: fatty acids, sterols, wax esters, fatty alcohols, triacylglycerols, etc. Any remains of soil were removed with an electric hand-drill. The sample was then grinded to the appropriate size in an agatha mortar (0.25 mm). Extraction with a the mixture chloroform/methanol (CHCl3:MeOH) (2:1 v/v) assisted by ultrasound. Derivatization of lipids to trimethylsilyl derivatives (TMS). The reaction tales place at 70 ºC for 30 min using N,O-bis-(trimethylsilyl) trifluoroacetamide (BSTFA) with 1 % trimethylchlorosilane (TMCS). The sample is solved in cyclohexane and then injected in GC-MS. Chromatographic separation is performed applying an adequate temperature programme. Gas chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) The analyses were performed using a using a gas chromatography equipment (model Thermo TraceGC Ultra) coupled to a Thermo DC Q II mass spectrometer. Autosampler Thermo Triplus (CICT, University of Jaén). The samples were introduced by on-column injection into a 15 m x 0.25 mm I.D. fused silica capillary column, coated with poly(dimethylsiloxane) stationary phase with 0.1 μm film thickness. Helium was used as the carrier gas (purity 99.99%). | |
High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Pottery. Analysis of triacylglycerols Destructive method for the identification of TAGs content. Any remains of soil were removed with an electric hand-drill. The sample was then grinded to the appropriate size in an agatha mortar (0.25 mm). Extraction with a the mixture chloroform/methanol (CHCl3:MeOH) (2:1 v/v) assisted by ultrasound. Derivatization is no needed. Lipid extract is solved in isopropanol and then injected in HPLC-APCI-MS. Chromatographic separation is performed applying an adequate mobile phase gradient (mixture of isopropanol and methanol). High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (HPLC-MS) Agilent 1290 Infinity HPLC system connected to an Agilent 6220 TOF (time-of-flight) mass spectrometer equipped with APCI (Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization) interface. (Departement of Physical and Analytical Chemistry, University of Jaén). Chromatographic column Zorbax Eclipse Plus C18 (150 mm x 4.6 mm, 1.8 μm particle size). |
































